How Long Does Earth Take To Travel Around The Sun? It takes Earth approximately 365.25 days to complete one orbit around the sun, also known as a sidereal year, a crucial concept for family travel planning and understanding seasonal changes; learn more on familycircletravel.net. Understanding this helps families plan vacations around school schedules and seasonal weather, creating memorable travel experiences. For families looking to maximize their travel adventures, grasping the duration of Earth’s orbit opens up a world of possibilities for planning family vacations, educational trips, and seasonal celebrations around the globe.
1. Understanding Earth’s Orbit
1.1. What is a Great Circle?
A great circle is an imaginary circle on a sphere’s surface, with its center coinciding with the sphere’s center. This concept is crucial in geography and navigation. Meridians, or lines of longitude, are great circles that pass through both the North and South Poles. Every point on Earth’s surface can have a meridian defined for it.
1.2. What are Terrestrial Coordinates?
Terrestrial coordinates are a system used to pinpoint locations on Earth’s surface. They consist of latitude and longitude:
- Longitude: Measures east-west position. The prime meridian, located at the old Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, serves as the 0-degree starting point. Longitude is expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds, ranging from 0 to 180 degrees eastward or westward from the prime meridian.
- Latitude: Measures north-south position. The equator, a great circle equidistant from the poles, is the starting point. Parallels, or lines of latitude, are circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is expressed as an arc between the equator and the parallel, as seen from Earth’s center.
Understanding these coordinates is essential for planning and navigating family trips.
1.3. Why are Terrestrial Coordinates Important for Spacecraft Navigation?
Spatial coordinates and timing conventions are essential for consistently pinpointing locations and motions of observers, natural objects within our solar system, and spacecraft journeying through interplanetary space or orbiting planets or other celestial bodies. Without these well-defined conventions, navigating the solar system would be impossible. Just imagine trying to find your way to Disney World without GPS – that’s how crucial these coordinates are for space travel.
2. Rotation vs. Revolution
2.1. What is the Difference Between Rotation and Revolution?
“Rotation” refers to an object’s spinning motion around its own axis, like a top spinning on a table. “Revolution” refers to an object’s orbital motion around another object, such as a planet orbiting a star.
2.2. How Does Earth’s Rotation Affect Our Daily Lives?
Earth rotates on its axis, completing one rotation approximately every 24 hours, which gives us day and night. This rotation influences weather patterns, ocean currents, and even our sleep cycles.
2.3. How Does Earth’s Revolution Affect Our Yearly Calendar?
Earth revolves around the Sun, completing one revolution in about 365.25 days, which defines a year. This revolution, combined with Earth’s axial tilt, causes the seasons.
3. Earth’s Rotation: The 24-Hour Day
3.1. How Long Does It Take for Earth to Rotate on its Axis?
The Earth rotates on its axis relative to the Sun every 24.0 hours mean solar time, with an inclination of 23.45 degrees from the plane of its orbit around the Sun. Mean solar time averages out variations caused by Earth’s non-circular orbit.
3.2. What is Sidereal Time?
Earth’s rotation relative to “fixed” stars (sidereal time) is 3 minutes 56.55 seconds shorter than the mean solar day, the equivalent of one solar day per year.
3.3. Why Does Earth Have an Inclination of 23.45 Degrees?
The Earth’s axial tilt of 23.45 degrees is responsible for the seasons. As Earth orbits the Sun, different parts of the planet receive more direct sunlight, leading to warmer temperatures in summer and cooler temperatures in winter. This tilt is a key factor in the diverse climates and ecosystems around the globe.
4. Precession of Earth’s Axis Over 26,000 Years
4.1. What is Precession?
Forces associated with the rotation of Earth cause the planet to be slightly oblate, displaying a bulge at the equator. The moon’s gravity primarily, and to a lesser degree the Sun’s gravity, act on Earth’s oblateness to move the axis perpendicular to the plane of Earth’s orbit. However, due to gyroscopic action, Earth’s poles do not “right themselves” to a position perpendicular to the orbital plane. Instead, they precess at 90 degrees to the force applied. This precession causes the axis of Earth to describe a circle having a 23.4 degree radius relative to a fixed point in space over about 26,000 years, a slow wobble reminiscent of the axis of a spinning top swinging around before it falls over.
4.2. How Does Precession Affect Our View of the Stars?
Because of the precession of the poles over 26,000 years, all the stars, and other celestial objects, appear to shift west to east at the rate of .014 degree each year (360 degrees in 26,000 years). This apparent motion is the main reason for astronomers as well as spacecraft operators to refer to a common epoch such as J2000.0.
4.3. What is Proper Motion?
Stars do have their own real motion, called proper motion. In our vicinity of the galaxy, only a few bright stars exhibit a large enough proper motion to measure over the course of a human lifetime, so their motion does not generally enter into spacecraft navigation. Because of their immense distance, stars can be treated as though they are references fixed in space. (Some stars at the center of our galaxy, though, display tremendous proper motion speeds as they orbit close to the massive black hole located there.)
4.4. How Does Precession Impact Family Travel?
While precession might seem like a distant astronomical concept, it has practical implications for long-term planning. Imagine wanting to see a specific constellation during a family camping trip. Because of precession, the position of stars changes slightly over long periods. So, the constellations you see today will not be in the exact same spot thousands of years from now.
5. Nutation: The Nodding Motion
5.1. What is Nutation?
Superimposed on the 26,000-year precession is a small nodding motion with a period of 18.6 years and an amplitude of 9.2 arc seconds. This nutation can trace its cause to the 5 degree difference between the plane of the Moon’s orbit, the plane of the Earth’s orbit, and the gravitational tug on one other.
5.2. How Does Nutation Affect Earth’s Axis?
Nutation causes a slight wobble in Earth’s axis, affecting the precision of astronomical measurements.
5.3. Why is Nutation Important for Scientific Measurements?
Scientists need to account for nutation when making precise measurements of celestial objects. Without considering this nodding motion, calculations could be slightly off, impacting everything from satellite positioning to understanding climate change.
6. Revolution of Earth: The 365-Day Year
6.1. How Long Does Earth Take to Revolve Around the Sun?
Earth revolves in orbit around the Sun in 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes with reference to the stars, at a speed ranging from 29.29 to 30.29 km/s.
6.2. What is a Leap Year?
The 6 hours, 9 minutes adds up to about an extra day every fourth year, which is designated a leap year, with the extra day added as February 29th.
6.3. What is Earth’s Orbit?
Earth’s orbit is elliptical and reaches its closest approach to the Sun, a perihelion of 147,090,000 km, on about January fourth of each year. Aphelion comes six months later at 152,100,000 km.
6.4. How Does Earth’s Revolution Impact Family Travel?
Earth’s revolution dictates the changing seasons, which significantly influence travel plans. Summer vacations are popular due to warm weather and school breaks, while winter holidays offer unique experiences like skiing and snowboarding. Understanding these seasonal changes helps families choose the best time to visit specific destinations.
7. Shorter-Term Polar Motion
7.1. What is the Chandler Wobble?
Aside from the long-term motions, the Earth’s rotational axis and poles have two shorter periodic motions. One, called the Chandler wobble, is a free nutation with a period of about 435 days.
7.2. What is Yearly Circular Motion?
There is also a yearly circular motion, and a steady drift toward the west caused by fluid motions in the Earth’s mantle and on the surface.
7.3. Who Tracks These Motions?
These motions are tracked by the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service, IERS.
8. Epochs: Snapshots in Time
8.1. What is an Epoch?
Because we make observations from Earth, knowledge of Earth’s natural motions is essential. As described above, our planet rotates on its axis daily and revolves around the Sun annually. Its axis precesses and nutates. Even the “fixed” stars move about on their own. Considering all these motions, a useful coordinate system for locating stars, planets, and spacecraft must be pinned to a single snapshot in time. This snapshot is called an epoch.
8.2. What is J2000.0?
By convention, the standard reference epoch is J2000.0, which refers to the mean equator and equinox of year 2000, nominally January 1st 12:00 hours Universal Time (UT). The “J” means Julian year, which is 365.25 days long. Only the 26,000-year precession part of the whole precession/nutation effect is considered, defining the mean equator and equinox for the epoch.
8.3. What was B1950.0?
The last epoch in use previously was B1950.0 – the mean equator and equinox of 1949, Dec. 31 22:09 UT, the “B” meaning Besselian year, the fictitious solar year introduced by F. W. Bessell in the 19th century. Equations are published for interpreting data based on past and present epochs.
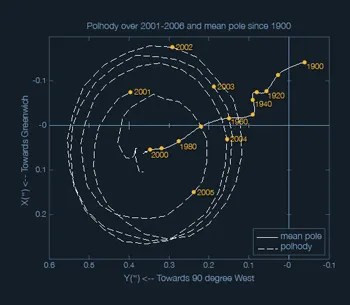 Movement of Earth's rotational poles 2001 to 2006, and the mean pole location from the year 1900 to 2000
Movement of Earth's rotational poles 2001 to 2006, and the mean pole location from the year 1900 to 2000
9. Making Sense of Earth’s Motions
9.1. Why is Understanding Earth’s Motions Important?
Given an understanding of the Earth’s suite of motions — rotation on axis, precession, nutation, short-term polar motions, and revolution around the Sun — and given knowledge of an observer’s location in latitude and longitude, meaningful observations can be made. This makes it possible to accurately navigate the Solar System.
9.2. How Do We Measure Spacecraft Speed?
For example, to measure the precise speed of a spacecraft flying to Saturn, you have to know exactly where you are on the Earth’s surface as you make the measurement, and then subtract out the Earth’s motions from that measurement to obtain the spacecraft’s speed.
9.3. How Do We Study Distant Stars?
The same applies if you are trying to measure the proper motion of a distant star — or a star’s subtle wobble, to reveal a family of planets.
10. Planning Family Travel with Earth’s Orbit in Mind
10.1. How Can You Plan a Trip Around the Seasons?
Understanding the length of Earth’s orbit and its impact on seasons allows you to plan trips that align with the best weather and activities for your chosen destination.
Seasonal Travel Ideas for Families
| Season | Destination Ideas | Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Spring | Amsterdam, Netherlands; Kyoto, Japan | Tulip festivals, cherry blossom viewing, cultural experiences |
| Summer | Orlando, Florida; San Diego, California | Theme parks, beach vacations, outdoor adventures |
| Autumn | New England, USA; Munich, Germany | Leaf peeping, Oktoberfest, historical sightseeing |
| Winter | Lapland, Finland; Banff, Canada | Northern Lights viewing, skiing, snowboarding, winter festivals |
10.2. How Can You Use Astronomy for Educational Travel?
Incorporate astronomical events into your travel plans for an educational and awe-inspiring experience.
10.3. How Can FamilyCircleTravel.net Help?
For more ideas and resources to plan your next family adventure, visit familycircletravel.net. We offer a wealth of information on destinations, activities, and travel tips to make your trip unforgettable.
11. The Search Intent Behind “How Long Does Earth Take to Travel Around the Sun”
11.1. Informational Intent:
Users want a simple, factual answer about the duration of Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
11.2. Educational Intent:
Parents and educators seek explanations suitable for children or students, often linked to science projects or schoolwork.
11.3. Travel Planning Intent:
Families planning vacations might use this information to understand seasonal changes and plan trips accordingly.
11.4. Astronomical Interest Intent:
Astronomy enthusiasts look for precise details and related concepts like sidereal years and orbital mechanics.
11.5. General Knowledge Intent:
Individuals seek to improve their general understanding of basic scientific facts.
12. Why Trust FamilyCircleTravel.net for Your Family Travel Needs?
12.1. Expert Advice
At familycircletravel.net, we understand the unique challenges and joys of family travel. That’s why we’re dedicated to providing you with expert advice, insightful tips, and comprehensive resources to help you plan the perfect trip. Whether you’re traveling with toddlers, teens, or multiple generations, our content is tailored to meet your family’s specific needs.
12.2. Curated Destinations
We meticulously curate a wide range of family-friendly destinations, from exciting theme parks to serene natural landscapes. Our detailed guides provide all the information you need to make informed decisions, including the best times to visit, must-see attractions, and recommended accommodations.
12.3. Practical Tips and Tricks
Traveling with family can be complex, but it doesn’t have to be stressful. We offer practical tips and tricks to streamline your travel process, from packing efficiently to managing budgets and keeping everyone entertained on the go.
12.4. Family-Focused Accommodations
Finding the right place to stay is crucial for a successful family vacation. We highlight hotels, resorts, and vacation rentals that cater to families, offering amenities like kids’ clubs, family suites, and convenient locations.
12.5. Engaging Activities
We suggest activities that appeal to all age groups, ensuring that everyone in your family has a memorable experience. Whether it’s exploring historical sites, enjoying outdoor adventures, or immersing yourselves in local culture, we’ve got you covered.
13. Call to Action: Start Planning Your Next Family Adventure Today!
13.1. Explore Destinations
Ready to create unforgettable memories with your loved ones? Visit familycircletravel.net today to explore our curated list of destinations. Discover hidden gems, popular attractions, and unique experiences that will delight every member of your family.
13.2. Get Inspired
Need some inspiration? Browse our travel stories and destination guides to spark your imagination. See how other families have explored the world and get ideas for your own adventures.
13.3. Plan Your Trip
Use our planning tools and resources to create a detailed itinerary. From booking flights and accommodations to arranging activities and transportation, we provide everything you need to plan a seamless and stress-free vacation.
13.4. Contact Us
Have questions or need personalized recommendations? Contact our team of travel experts. We’re here to help you every step of the way, ensuring that your family vacation is everything you’ve dreamed of and more.
13.5. Stay Connected
Sign up for our newsletter to receive the latest travel news, exclusive deals, and insider tips. Follow us on social media to stay connected with a community of like-minded families who share a passion for travel.
14. Contact Information
For any inquiries or assistance, feel free to reach out to us:
- Address: 710 E Buena Vista Dr, Lake Buena Vista, FL 32830, United States
- Phone: +1 (407) 824-4321
- Website: familycircletravel.net
15. FAQ: Earth’s Orbit and Family Travel
15.1. How Long Does Earth Take to Travel Around the Sun?
Earth takes approximately 365.25 days to complete one orbit around the sun.
15.2. What is a Leap Year and Why Do We Have It?
A leap year occurs every four years to account for the extra 0.25 days in Earth’s orbit, adding an extra day (February 29th) to keep our calendar aligned with the seasons.
15.3. How Does Earth’s Orbit Affect the Seasons?
Earth’s tilted axis and its orbit around the sun cause different parts of the planet to receive more direct sunlight at different times of the year, creating the seasons.
15.4. What is the Difference Between Rotation and Revolution?
Rotation is the spinning of Earth on its axis, which causes day and night, while revolution is Earth’s orbit around the sun, which defines a year.
15.5. What is the Significance of the Prime Meridian?
The prime meridian is the 0-degree line of longitude, used as the starting point for measuring east-west locations on Earth.
15.6. How Does Precession Affect Our View of the Stars?
Precession causes a slow wobble in Earth’s axis, leading to a gradual shift in the apparent positions of stars over thousands of years.
15.7. What is Nutation and Why is it Important?
Nutation is a small nodding motion superimposed on precession, affecting the precision of astronomical measurements and requiring scientists to account for it in their calculations.
15.8. How Can I Use the Knowledge of Earth’s Orbit to Plan Family Vacations?
Understanding Earth’s orbit and its impact on seasons helps families plan trips that align with the best weather and activities for their chosen destinations.
15.9. Where Can I Find More Information About Family Travel Destinations?
Visit familycircletravel.net for a wealth of information on family travel destinations, activities, and travel tips.
15.10. What are Some Educational Travel Ideas for Families?
Incorporate astronomical events, historical sites, and cultural experiences into your travel plans for educational and enriching family trips.
By understanding how long Earth takes to travel around the sun and the related astronomical concepts, families can plan more informed and enjoyable travel experiences. Visit familycircletravel.net for more inspiration and resources to make your next trip unforgettable!

